|
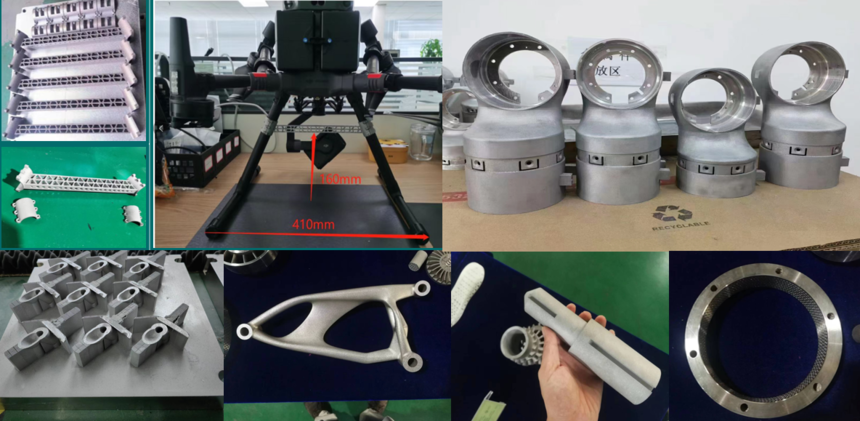
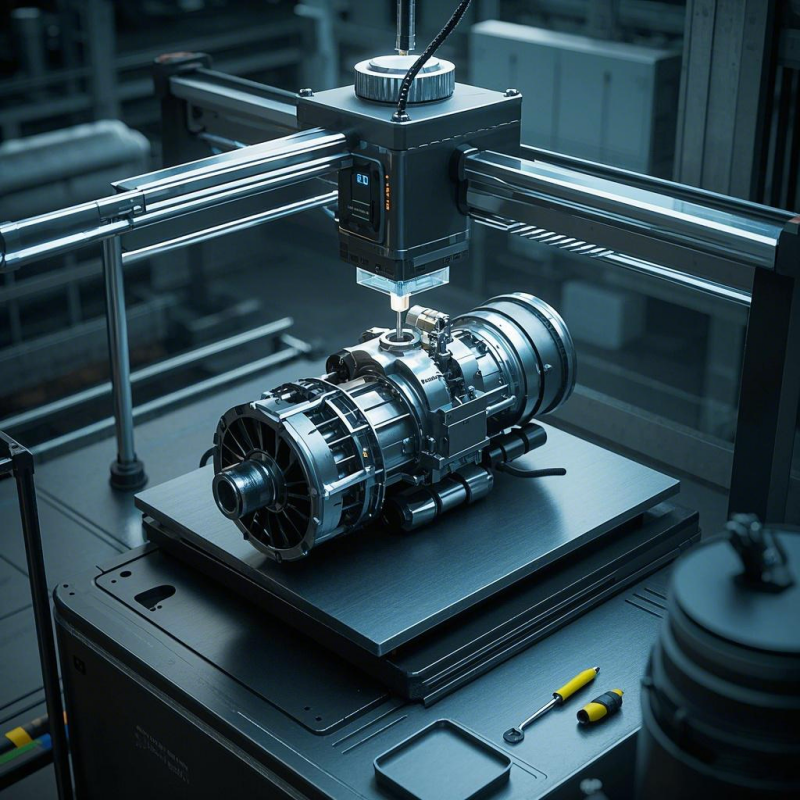
Metal parts3D printed metal components procedure uses advanced techniques like powder-bed fusion (e.g., selective laser melting) or direct energy deposition,
where metal powders or wires are melted and fused under precise
computer control. Unlike traditional subtractive methods, it offers
unparalleled design freedom, enabling complex geometries, lightweight
structures, and functional integration impossible with conventional
machining. 
Collect
Features
Details
The development potential of 3D printed metal components is revolutionizing advanced manufacturing. Powder-bed fusion and direct energy deposition technologies enable intricate, high-strength parts with design freedom, reducing material waste and lead times. Aerospace and automotive sectors adopt lightweight metal components for fuel efficiency, while medical applications leverage biocompatible implants. The global market is projected to surpass $15 billion by 2030, driven by demand for titanium, aluminum, and nickel alloys in extreme environments. Innovations in hybrid manufacturing and multi-metal printing expand functional prototypes and end-use products. As scalability improves and costs decline, metal additive manufacturing will disrupt supply chains, enabling localized production of durable, complex parts across energy, defense, and consumer industries.
Reference videos of application Metal cubic web structure part Irregular shape metal part 1 Irregular shape metal part 2 |